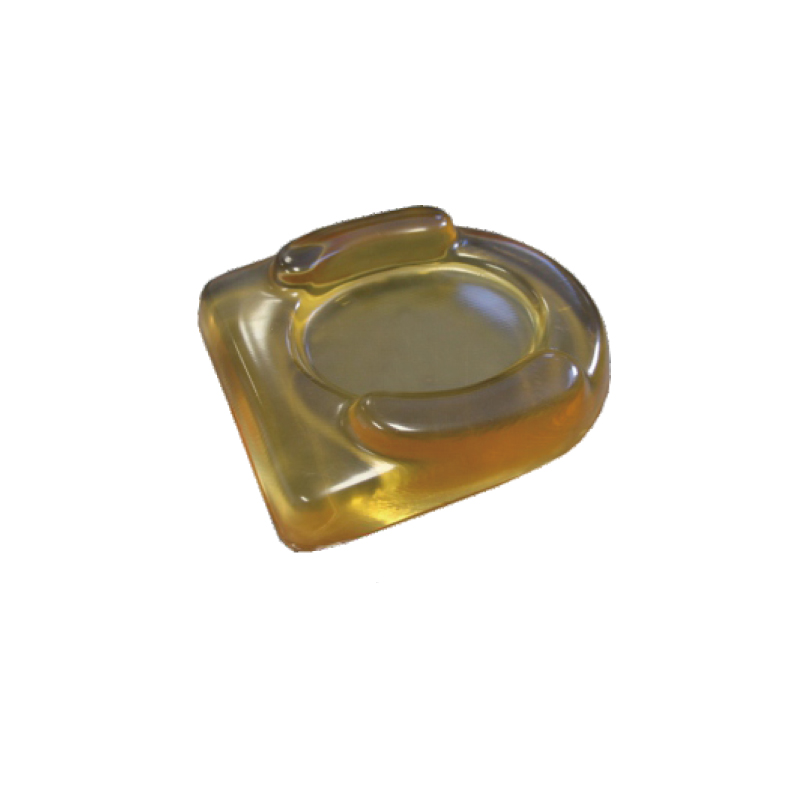
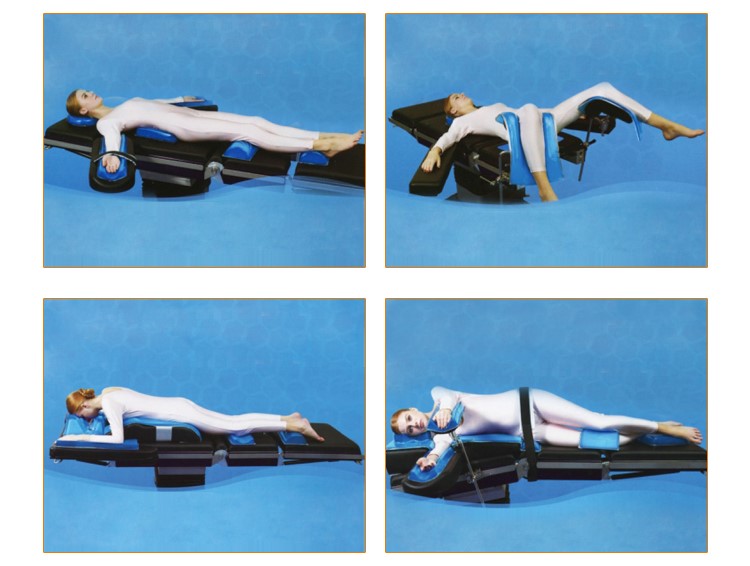
Ophthalmic head positioner ORP-OH-01
Ophthalmic head positioner
Model: ORP-OH-01
Function
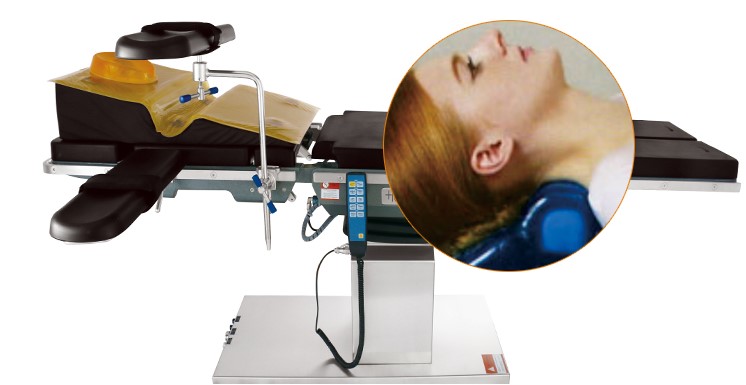
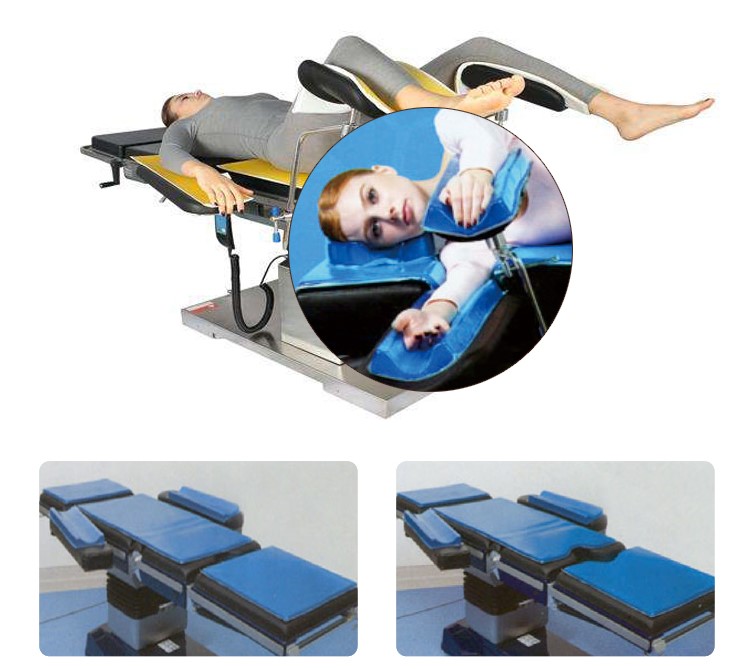
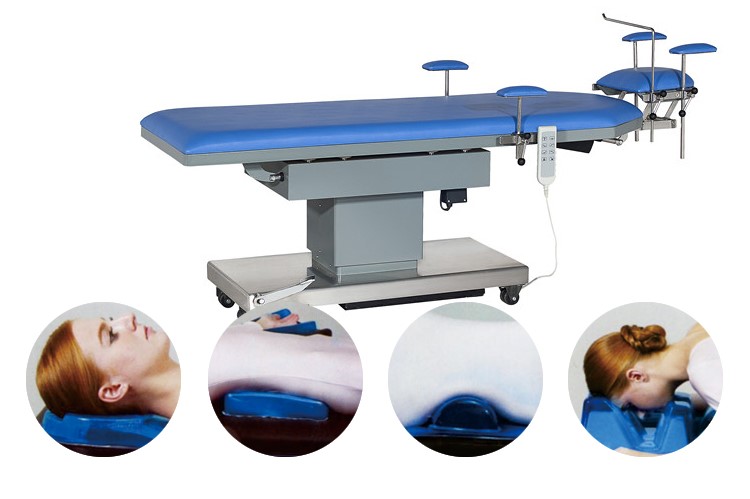
1. To stabilize patient's head. Applied to ophthalmology, ENT and plastic surgery in supine position
2. To protect and support patient's head in ophthalmic, oral, facial and ENT surgery
3. Keep patient comfort under anesthesia.
4. Centering dish minimizes movement in conscious sedation
Dimension
28.5 x 25 x 6.5cm
Weight
2.7kg
Product parameters
Product Name: Positioner
Material: PU Gel
Definition: It is a medical device which is used in an operating room to protect patient from pressure sores during surgery.
Model: Different positioners are used for different surgical positions
Color: Yellow, blue, green. Other colors and sizes can be customized
Product characteristics: Gel is a kind of high molecular material, with good softness, support, shock absorption and compression resistance, good compatibility with human tissues, X-ray transmission, insulation, non-conductive, easy to clean, convenient to disinfect, and does not support bacterial growth.
Function: Avoid pressure ulcer caused by long operation time
Product characteristics
1. The insulation is non-conductive, easy to clean and disinfect. It does not support bacterial growth and has good temperature resistance. The resistance temperature ranges from -10 ℃ to +50 ℃
2. It provides patients with good, comfortable and stable body position fixation. It maximizes the exposure of the surgical field, reduce the operation time, maximize the dispersion of pressure, and reduce the occurrence of pressure ulcer and nerve damage.
Cautions
1. Do not wash the product. If the surface is dirty, wipe the surface with a wet towel. It can also be cleaned with neutral cleaning spray for better effect.
2. After using the product, please clean the surface of the positioners on time to remove dirt, sweat, urine, etc. The fabric can be stored in a dry place after drying in a cool place. After storage, do not put heavy objects on top of the product.
Ophthalmic head positioner is suitable for ophthalmic surgery.
Ophthalmic surgery
Ophthalmology is the branch of medicine that deals with the anatomy, physiology and disease of the eye and visual system. Ophthalmologic surgery is a surgical procedure performed on the eye or any part of the eye. Surgery on the eye is routinely performed to repair retinal defects, remove cataracts or cancer, or to repair eye muscles. The most common purpose of ophthalmologic surgery is to restore or improve vision.
The surgeon, operating room nurses, and an anesthesiologist are present for ophthalmologic surgery. For many eye surgeries, only a local anesthetic is used, and the patient is awake but relaxed. The patient’s eye area is scrubbed prior to surgery, and sterile drapes are placed over the shoulders and head. Heart rate and blood pressure are monitored throughout the procedure. The patient is required to lie still and for some surgery, especially refractive surgery, he or she is asked to focus on the light of the operating microscope. A speculum is placed in the eye to hold it open throughout surgery.
Common ophthalmologic surgery tools include scalpels, blades, forceps, speculums, and scissors. Many ophthalmologic surgeries now use lasers, which decrease the operating time as well as recovery time.
Surgeries requiring suturing can take as long as two to three hours. These intricate surgeries sometimes require the skill of a corneal or vitreo-retinal specialist, and require the patient to be put under general anesthesia.
Refractive surgeries
Refractive surgeries use an excimer laser to reshape the cornea. The surgeon creates a flap of tissue across the cornea with an instrument called a microkeratome, ablates the cornea for about 30 seconds, and then replaces the flap. The laser allows this surgery to take only minutes, without the use of stitches.
Trabeculectomy
Trabeculectomy surgery uses a laser to open the drainage canals or make an opening in the iris to increase outflow of aqueous humor. The purpose is to lower intraocular pressure in the treatment of glaucoma.
Laser photocoagulation
Laser photocoagulation is used to treat some forms of wet age-related macular degeneration. The procedure stops leakage of abnormal blood vessels by burning them to slow the progress of the disease.